Last month we released a new version of our popular run-anything-as-a-windows-service software, AlwaysUp. Everything was going smoothly — until we encountered a very alarming situation while testing the new software on Windows 10!
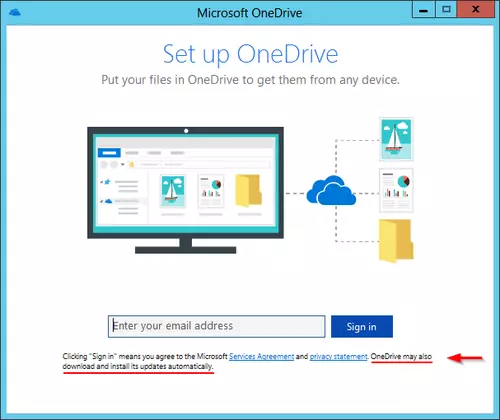
After downloading the new AlwaysUp installation executable with Microsoft Edge, the browser asserted that “AlwaysUp_Installer.exe is not commonly downloaded and may harm your computer”. WHAT??
Clicking the Actions button gave us the option to “Run Anyway”, and the installation completed without further incident, but the whole experience left our team worried and full of questions. Specifically:
- Why did this suddenly start happening?
- How will our customers react to Microsoft’s unfounded suspicions?
- And most importantly, how do we get rid of the chilling warnings?
SmartScreen Complains because our Software is “New”
Apparently we’re not the only developers tormented by SmartScreen. Warnings are common, especially for small software companies like ours. The “Criticism” section of the Wikipedia article on SmartScreen Filter says it best:
SmartScreen Filter creates a problem for small software vendors when they distribute an updated version of installation or binary files over the internet. Whenever an updated version is released, SmartScreen responds by stating that the file is not commonly downloaded and can therefore install harmful files on your system.
Only a Few Customers are Blocked by SmartScreen Filter
To date, only one customer has asked about SmartScreen’s warning. We had expected hundreds! Fortunately there are a few reasons why many customers aren’t being tripped up by Microsoft’s overly cautious approach:
- Our products are digitally signed for security and authenticity. SmartScreen takes this as a positive sign and is likely to avoid prompting all customers all the time.
- Prior to Windows 8, SmartScreen Filter was a part of Internet Explorer. Thus customers using Chrome or Firefox on Windows 7 and Server 2008 will never encounter SmartScreen warnings.
- After testing downloads on Windows 8, 10 and Windows Server 2012 and 2016, we only received warnings on Windows 10 with Edge.
So it seems that SmartScreen warnings are largely limited to customers using Internet Explorer or Edge. Metrics gathered from our website (via the incredibly useful StatCounter) tell us that only about 11% of all visitors are using those browsers:
Time (and Good Behavior) will Disarm SmartScreen Filter
We hoped for a simple solution: Inform Microsoft that our software is 100% safe and they would promptly update their SmartScreen database to remove all warnings. All would be right with the world. But SmartScreen doesn’t work like that.
SmartScreen is reputation based. Each time someone downloads our software package and declares that it is safe to install, that executable gains some positive reputation. Once enough people have successfully installed and the accumulated reputation crosses some magic threshold, the warnings disappear. Only an established track record of doing no harm will halt the SmartScreen dogs.
Indeed, after a couple of weeks the warnings for AlwaysUp version 10 seems to have gone away:
Yay!